KeblaOS







This chapter’s content was one of my main headech.
According IA32 Intel Systems Programming Documentation, Volume 3A, Chapter - 3 Different types Registers in x86_64
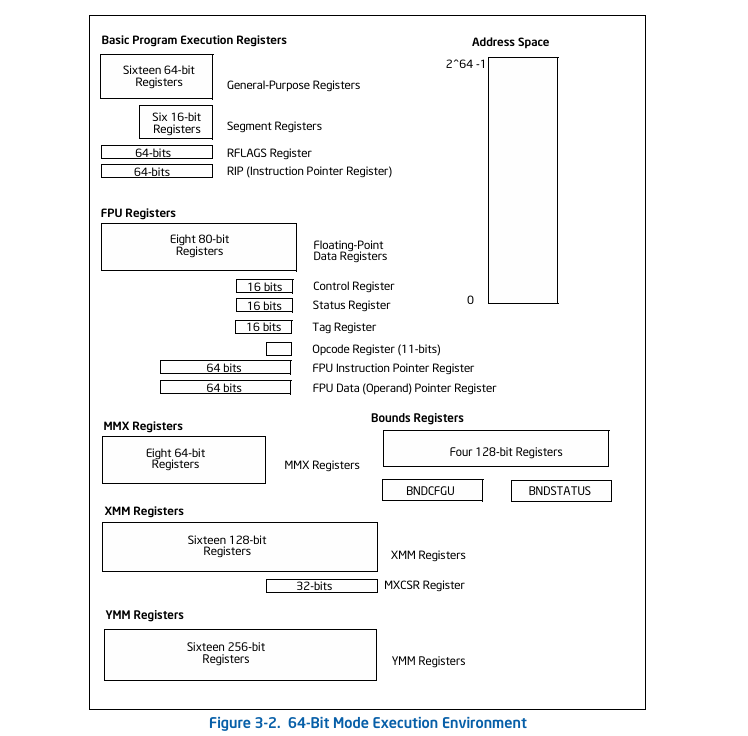
I have written following registers structure to store different registers states in utl.h
typedef struct registers
{
uint64_t ds, es, fs, gs; // Segment registers
uint64_t r15, r14, r13, r12, r11, r10, r9, r8; // General-purpose registers
uint64_t rdi, rsi, rbp, rdx, rcx, rbx, rax; // General-purpose registers
uint64_t int_no, err_code; // Interrupt number and error code
uint64_t iret_rip, iret_cs, iret_rflags, iret_rsp, iret_ss; // CPU state
} registers_t;
Memory map by Limine Bootloader => Physical Memory Manager => Paging => Virtual Memory manager => Static kernel Heap => Dynamic Kernel Heap allocation.
- Physical memory Manager :
In KeblaOS I am using x86 architecture 64 Bit Flat memory Model.
Here I am using bitmap to store status of a 4KB Physical Frame. Here I am showing a basic example
Index | 0| 1| 2| 3| 4| 5|....|60|61|62|63|
------------------------------------
nth Bit state | 0| 0| 1| 0| 0| 1|....| 0| 0| 0| 0| 64 Bit
Here 64 Bit valu can store 64 x 4 KB = 256 KB of memory states.
Here nth row 3rd and 5th frame are using. So here Index is n and offset are 3 and 4 respectively.
So the physical address of nth row 3rd bit = n644 + 34 = (n64 + 3)*4
in general from row and offset to bit_no
bit_no = (n*64 + offset) * frame_size
Oppositely I can derive row and offset from bit_no
row = (int) bit_no / 64
offset = (int) bit_no % 64
frame_size = 1KB = 1024 = 0x1000
Here I am going to implement 4Level Paging which will support 4KB Paging.So I am using 4KB Physical Frame.
So I am using following Macros
#define FRAME_SIZE 0x1000
#define BIT_SIZE 64
// Converting Bit no to index and offset
#define INDEX_FROM_BIT_NO(x)(x / BIT_SIZE)
#define OFFSET_FROM_BIT_NO(x)(x % BIT_SIZE)
// Converting index and offset to bit not
#define GET_BIT_NO(index, offset)(index*BIT_SIZE+offset)
// Converting Bit no to physical start address
#define GET_FRAME_ADDRESS(bit_no)(bit_no*FRAME_SIZE)
The all physical frames starts from PHYSICAL_PLACEMENT_ADDRESS and Maximum Placebale address. Which may set by Limine Bootloader memory map
#define PHYSICAL_PLACEMENT_ADDRESS 0x100000 // 1MB
#define PHYSICAL_END_ADDRESS 0x500000 // 5 MB
Now all physical frames allocated from PHYSICAL_PLACEMENT_ADDRESS address.
References :
-
https://wiki.osdev.org/Memory_management
-
http://www.osdever.net/tutorials/view/memory-management-1
-
https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/developer/articles/technical/intel-sdm.html
© 2025 KeblaOS Project. All rights reserved.